Chromosome-level genome reference and genome editing of the tea geometrid
Time:2021/3/19
Information: Molecular Ecology Resource 19 March 2021 https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-0998.13385
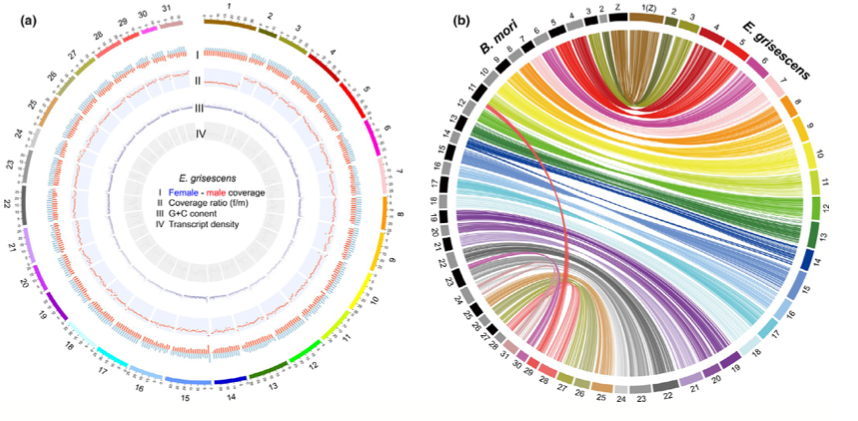
The tea geometrid is a destructive insect pest on tea plants, which seriously affects tea production in terms of both yield and quality and causes severe economic losses. The tea geometrid also provides an important study system to address the ecological adaptive mechanisms underlying its unique host plant adaptation and protective resemblance. In this study, we fully sequenced and de novo assembled the reference genome of the tea geometrid, Ectropis grisescens, using long sequencing reads. We presented a highly continuous, near-complete genome reference (787.4 Mb; scaffold N50: 26.9 Mb), along with the annotation of 18,746 protein-coding genes and 53.3% repeat contents. Importantly, we successfully placed 97.8% of the assembly in 31 chromosomes based on Hi-C interactions and characterized the sex chromosome based on sex-biased sequencing coverage. Multiple quality-control assays and chromosome-scale synteny with the model species all supported the high quality of the presented genome reference. We focused biological annotations on gene families related to the host plant adaptation and camouflage in the tea geometrid and performed comparisons with other representative lepidopteran species. Important findings include the E. grisescens-specific expansion of CYP6 P450 genes that might be involved in metabolism of tea defensive chemicals and unexpected massive expansion of gustatory receptor gene families that suggests potential polyphagy for this tea pest. Furthermore, we developed an efficient genome editing system based on CRISPR/Cas9 technology and successfully implement mutagenesis of a Hox gene in the tea geometrid. Our study provides key genomic resources both for exploring unique mechanisms underlying the ecological adaptation of tea geometrids and for developing environment-friendly strategies for tea pest management.