| Jump to section |
Basic information | Assembly statistics | PAV Calling | Tree |
| PCA | Admixture | Selection:Assamica and Sinensis | Selection: GO enrichment |
Basic information
Pan-genome can better reflect the genetic information of a species. From more than 600 global tea plant sequencing results, we screened the individuals that best represented the cultivated tea species, performed genome sequencing and constructed the tea plant pan-genome. The current version of the tea plant pan-genome is constructed from more than 200 global tea resources.
Method:
Pan-genome construction.Raw reads were processed to remove duplicated read pairs and yielded unique read pairs using Nubeam-dedup. The resulting reads were then processed to trim adapters and low-quality sequences using Trimmomatic (Version: 0.39) with parameters ‘SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 MINLEN:50’. The final cleaned reads of each sample were de novo assembled using Megahit (Version: v1.2.9) with default parameters. The assembled contigs with lengths bigger than 500 bp were kept and then aligned to the YK-10 reference genomes using Mummer (Version: 4.0.0beta2) . If the continuous alignment longer than 300 bp with sequence identity higher than 86%, then the alignment was labeled as a reliable alignment. Contigs with no reliable alignments were kept as unaligned contigs. For contigs containing the reliable alignments, if they also contained continuous unaligned regions longer than 500 bp, the unaligned regions were extracted as unaligned sequences. The unaligned contigs and unaligned sequences (>500 bp) were then searched against the GenBank nucleotide database using blastn (Version: 2.9.0+). Sequences with best hits from outside the green plants, or covered by known plant mitochondrial or chloroplast genomes, were removed. The cleaned nonreference sequences from all accessions were combined. The redundant sequences were removed using CD-HIT (Version: 4.8.1) with an identity threshold of 90%. The resulting non-redundant sequences and the reference YK-10 genome were merged as the pan-genome.
Annotation of the pan-genome.A custom repeat library was constructed by screening the pan-genome using EDTA (Version: v1.9.6) and used to screen the non-reference genome to identify repeat sequences using RepeatMasker (Version: 4.1.2-p1). Protein-coding genes were predicted from the repeat-masked non-reference genome using BRAKER (Version: 2.1.6) with two lines. One of the lines was running BRAKER with RNA-Seq data. RNA-seq data included illumina transcriptome for tender, old and normal leaves sequencing in our paper and reads of 40 tea samples downloaded from NCBI. The reads were cleaned using Trimmomatic (Version: 0.39) with parameters ‘SLIDINGWINDOW:4:15 MINLEN:70’ and aligned to the pan-genome with HISAT2 (Version: 2.2.0). And then the alignments were converted to a hint file for AUGUSTUS in gff format. All gff files were merged and fed to BRAKER. Another line was running BRAKER with OrthoDB Viridiplantae protein database. Two lines’ results were then combined using TSEBRA (https://github.com/Gaius-Augustus/TSEBRA). The genes were filtered if the proportion of repeat sequences in gene sequences greater than 50% or CDS sequence length less than 300 nt.
Gene functions were assigned according to the best match alignment using blastp against KEGG databases. InterProScan functional analysis and Gene Ontology IDs were obtained using InterProScan. The pathway to which the gene might belong was derived from the matching genes in KEGG.
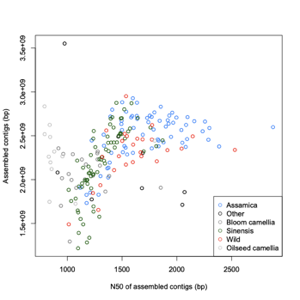
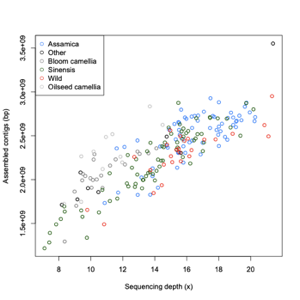
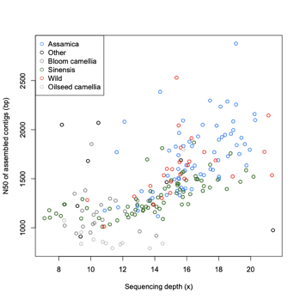
Assembly statistics
| Group | Number |
|---|---|
| Other | 8 |
| Bloom camellia | 21 |
| Oilseed camellia | 12 |
| Wild | 26 |
| Assamica | 68 |
| Sinensis | 71 |
| Total | 106 |
PAV Calling
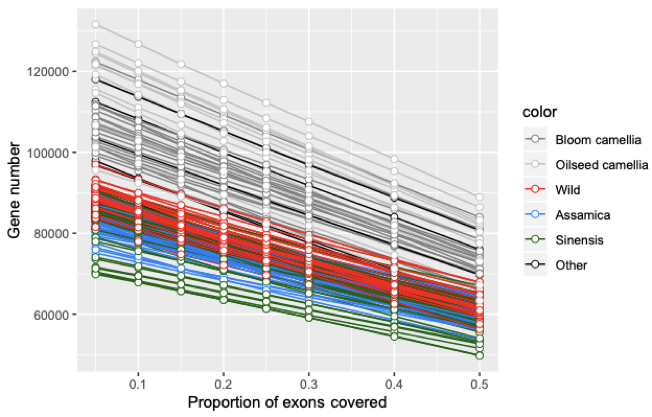
PAV calling - Gene number under different proportion of exons covered(select 0.2)
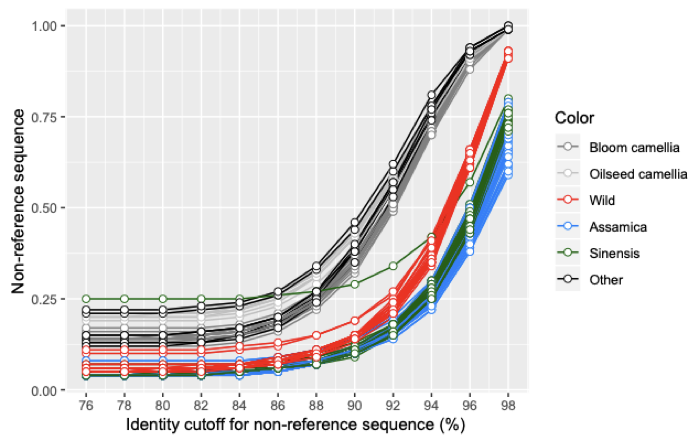
Un-alignment percnet
PAV calling - Modeling
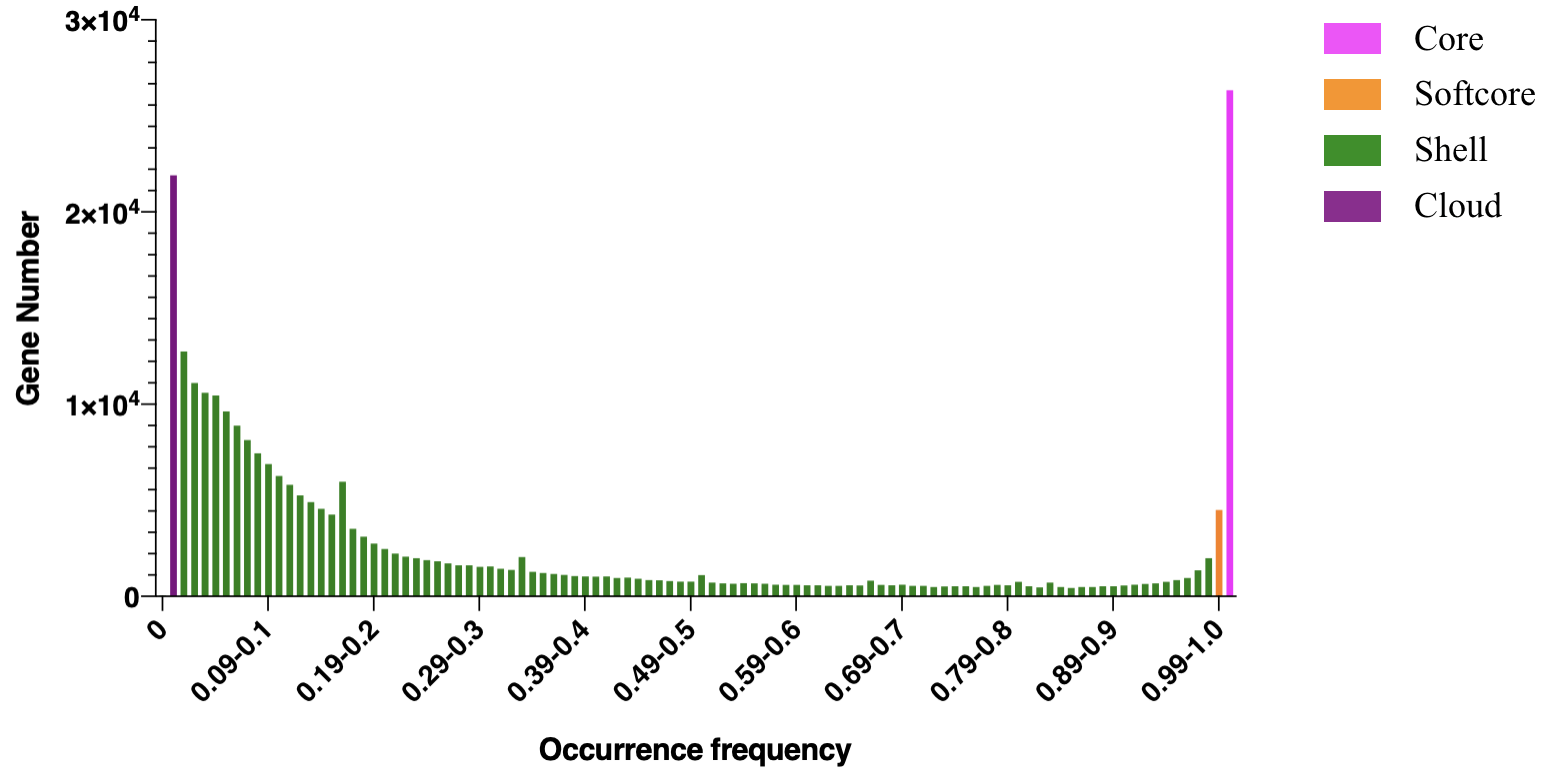
Occurrence frequency
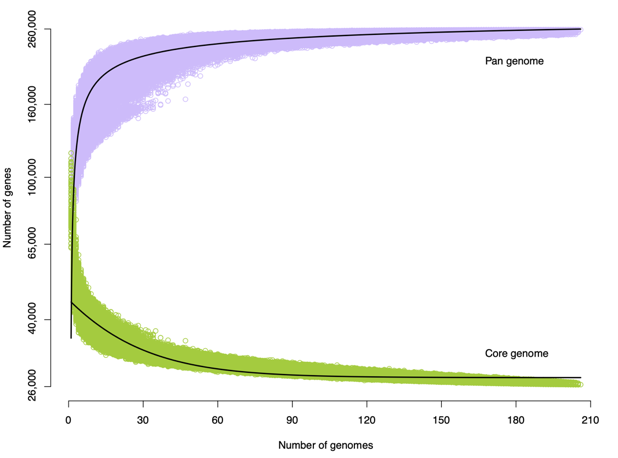
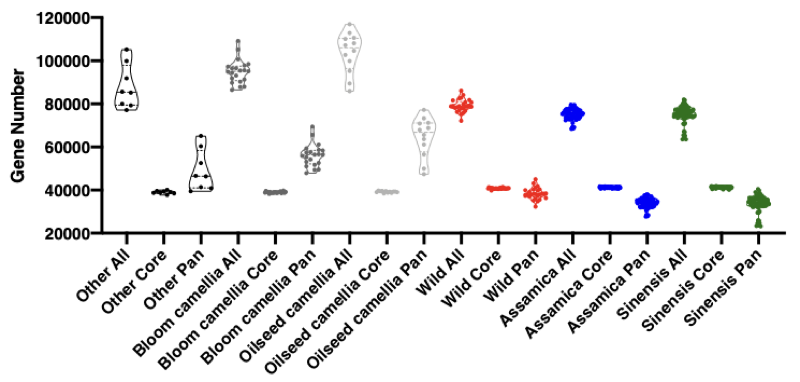
PAV calling - Gene number for core and pan genome
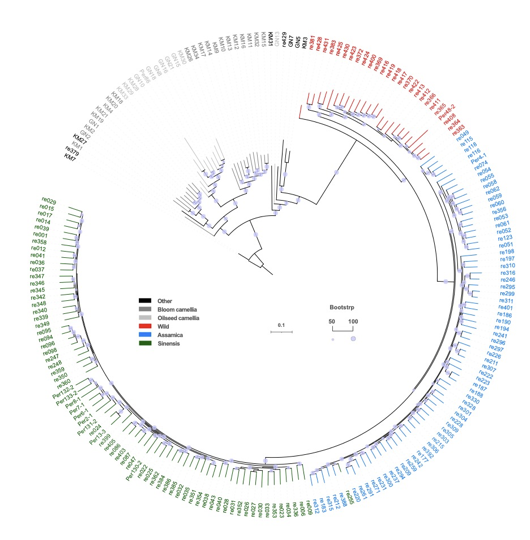
Tree
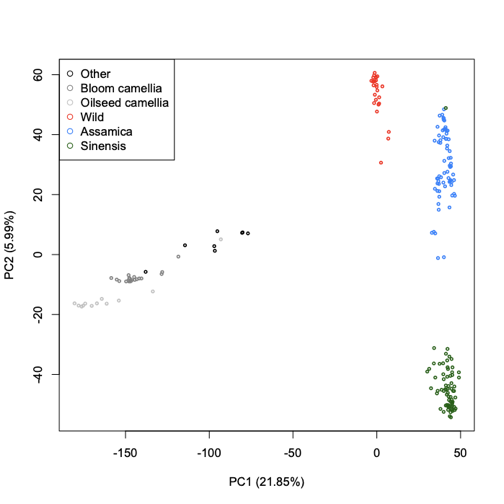
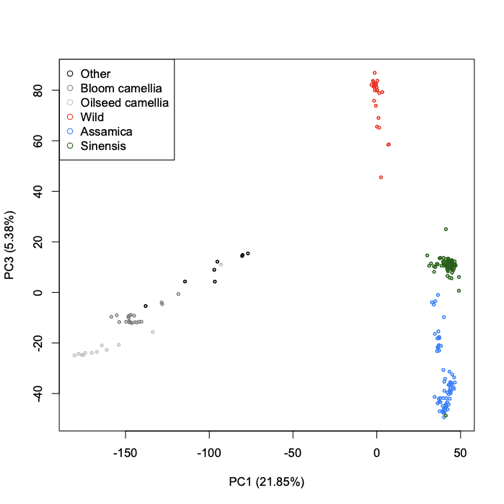
PCA


Admixture

Selection:Assamica and Sinensis

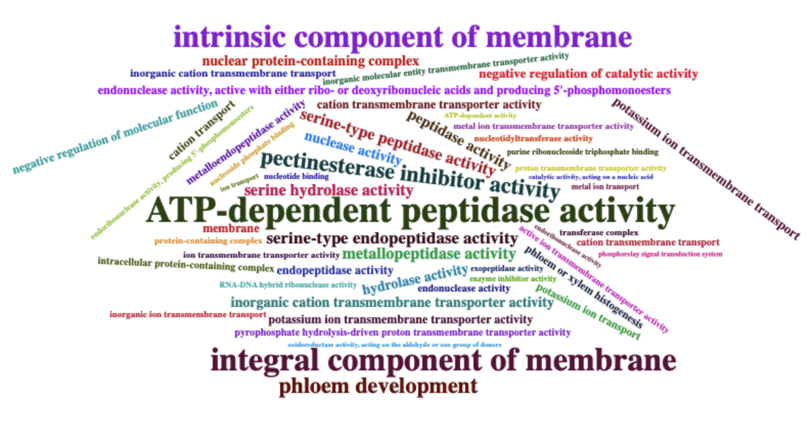
Selection:GO enrichment
Selection - GO enrichment - Assamica vs Sinensis

Selection - GO enrichment - Sinensis vs Assamica

Selection - GO enrichment - Bloom camellia vs Oilseed camellia

Selection - GO enrichment - Oilseed camellia vs Bloom camellia